Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 U
U )O
)O
Nakamichi, Shinya; Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Nelson, A. T.*; McClellan, K. J.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 535, p.152188_1 - 152188_8, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:75.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen-to-metal ratio (O/M) of uranium and plutonium mixed oxide depends on its oxygen partial pressure. To attain the desirable microstructure and O/M ratio of sintered pellets, it is important to investigate the relation between the sintering behavior and the atmosphere of sintering process. In this study, sintering behavior of (Pu U
U )O
)O and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O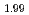 in controlled po
in controlled po atmosphere were investigated. It was found activation energy of (Pu
atmosphere were investigated. It was found activation energy of (Pu U
U )O
)O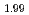 was higher than that of (Pu
was higher than that of (Pu U
U )O
)O . On the other hand, it was observed grain growth during sintering was suppressed in hypo-stoichiometric composition.
. On the other hand, it was observed grain growth during sintering was suppressed in hypo-stoichiometric composition.
Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko; Nozaki, Takahiro*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 465, p.840 - 842, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential of a prototypic Mo-cermet fuel containing PuO was experimentally determined. It was shown that the oxygen potentials of Mo-cermet fuel containing PuO
was experimentally determined. It was shown that the oxygen potentials of Mo-cermet fuel containing PuO were the same as those of pure PuO
were the same as those of pure PuO . It was also confirmed that the gradual oxidation of the Mo matrix occurred only above the oxygen potential of Mo/MoO
. It was also confirmed that the gradual oxidation of the Mo matrix occurred only above the oxygen potential of Mo/MoO . It is concluded that the oxidation-reduction behavior of the Mo-cermet fuel can be evaluated individually for each phase of actinides oxide and Mo matrix. Better phase structures of the Mo-cermet fuel for taking full advantage of the oxidation-reduction controllability were suggested by the confinement of the actinides oxide phase with Mo.
. It is concluded that the oxidation-reduction behavior of the Mo-cermet fuel can be evaluated individually for each phase of actinides oxide and Mo matrix. Better phase structures of the Mo-cermet fuel for taking full advantage of the oxidation-reduction controllability were suggested by the confinement of the actinides oxide phase with Mo.
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Takano, Masahide; Kurata, Masaki; Arita, Yuji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 464, p.270 - 274, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sato, Isamu; Onishi, Takashi; Tanaka, Kosuke; Iwasaki, Maho; Koyama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 461, p.22 - 28, 2015/06
We observed one of the simplified processes by conducting primitive experiments. CsI was heated at 1323 K to be vaporized and deposited on sampling parts with a temperature range of 1023 - 423 K and then B O
O was vaporized at 1973 K to be reacted with Cs/I there. After heating tests, each sampling part was soaked into alkali water to dissolve the surface-deposits for ICP-MS analysis. The results showed that CsI deposited at the sampling parts kept above approx. 850 K was striped by B
was vaporized at 1973 K to be reacted with Cs/I there. After heating tests, each sampling part was soaked into alkali water to dissolve the surface-deposits for ICP-MS analysis. The results showed that CsI deposited at the sampling parts kept above approx. 850 K was striped by B O
O vapour. This behaviour will be thermodynamically discussed to study the Cs/I/B chemistry in the severe accidents.
vapour. This behaviour will be thermodynamically discussed to study the Cs/I/B chemistry in the severe accidents.
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
The diffusion couples of (U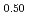 Pu
Pu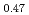 Am
Am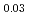 )O
)O and UO
and UO were annealed at 1873K in an atmosphere of
were annealed at 1873K in an atmosphere of  G
G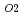 that correspond to O/M = 2.00 or 1.96, and the concentration profile of each actinide elements around the interface was measured with EPMA. It was clearly found that the diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, for O/M = 1.96, grain boundary and bulk diffusions of these actinides were not clearly observed.
that correspond to O/M = 2.00 or 1.96, and the concentration profile of each actinide elements around the interface was measured with EPMA. It was clearly found that the diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, for O/M = 1.96, grain boundary and bulk diffusions of these actinides were not clearly observed.
 in oxygen partial pressure controlled atmosphere
in oxygen partial pressure controlled atmosphereKato, Masato; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; McClellan, K.*; Nelson, A.*
no journal, ,
Thermal expansion of MOX was measured as a function of O/M ratio. The measurements of the thermal expansion and O/M were carried out with dilatometer and thermo gravimeter, respectively, in cooling process of 4 K/min. Oxygen potential of MOX has been measured, and the correlation was derived to represent the relationship between oxygen potential and O/M ratio. The P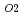 in the atmosphere was controlled according to the previous data which were controlled by adjusting PH
in the atmosphere was controlled according to the previous data which were controlled by adjusting PH /PH
/PH O ratio. It was confirmed to hold constant O/M ratio during the measurements by thermo-gravimetry. Thermal expansion of (U
O ratio. It was confirmed to hold constant O/M ratio during the measurements by thermo-gravimetry. Thermal expansion of (U Pu
Pu )O
)O increased with increasing the deviation x. The correlation to represent the thermal expansion was derived with Pu content and O/M ratio. The thermal expansion coefficients are consistent with those of PuO
increased with increasing the deviation x. The correlation to represent the thermal expansion was derived with Pu content and O/M ratio. The thermal expansion coefficients are consistent with those of PuO .
.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nogiwa, Kimihiro*; Sakakibara, Yasuhide*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
no journal, ,
Analyses on fracture behavior of cast duplex stainless steels sampled from piping of primary loop recirculation system of JAEA's nuclear reactor Fugen were performed. The samples were composed of primary austenite phase, and minor ferrite phase with from a few to few tens percent of volume fraction. It is known that thermal aging at about 300-500 C causes hardening of only the ferrite phase. Therefore, electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) analysis, which can observe individually the properties of the two phases, was applied so as to reveal its fracture mechanism. The results indicated that the crystallographic orientation relationship between the austenite and ferrite was hybrid, and that the Charpy absorbed energy depended on the deformation behavior of not only the austenite phase but also the minor ferrite phase near the fracture surface.
C causes hardening of only the ferrite phase. Therefore, electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) analysis, which can observe individually the properties of the two phases, was applied so as to reveal its fracture mechanism. The results indicated that the crystallographic orientation relationship between the austenite and ferrite was hybrid, and that the Charpy absorbed energy depended on the deformation behavior of not only the austenite phase but also the minor ferrite phase near the fracture surface.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Katsuyama, Jinya; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Abe, Yosuke; Nagase, Fumihisa
no journal, ,
In existing severe accident code, rupture of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) lower head after melt down of core is analyzed using the simple model like the Larson-Miller model. It is difficult to evaluate the local deformation and rupture behavior for the actual lower head with such a simple model. Therefore, in order to predict the real position of molten fuel outside pressure vessel, it is necessary to evaluate rupture time and rupture behavior of RPV lower head of BWR precisely.Re-evaluation of materials data such as mechanical properties, creep deformation/rupture properties is made for low alloy steel, Ni-based alloy and stainless steels based on past research activities. To expand materials database and verify the creep constitutive equation and rupture model, we started obtaining the materials data under uniaxial and multi-axial stress conditions at high temperature near melting point. To investigate the inhomogeneous temperature and stress distribution by geometrical complex of BWR lower head, the detailed 3D model of RPV lower head with control rod guide tubes (CRGTs) and shroud supports are constructed and the 3D thermal hydraulic analysis of simulated molten pool and creep deformation analysis of lower head are performed using ANSYS Fluent / Mechanical finite element code. It is found that the possibility of failure mode for BWR lower head are both the penetration failure which is melt-through or drop-away of the guide tube, local rupture and global rupture of lower head by creep deformation mechanism and the melting collapse mechanism due to different boundary conditions.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
Since grain-boundary (GB) embrittlement by phosphorus (P) under irradiation is a crucial problem in steels, it is necessary to evaluate irradiation-induced P GB segregation in order to secure the integrity of nuclear structural materials. Recently, partial diffusion coefficients including the vacancy (V) drag effect, which are obtained by the kinetic Monte Carlo method incorporating the barrier energy estimated by the first-principles calculation, are built into the diffusion rate model, and the model is applied to the evaluation of the P GB segregation. Since the amount of V is affected by temperature, we evaluated the P GB segregation by the model. As a result, although the model could not simulate the increase of P GB segregation in the high temperature region which is shown by the McLean's diffusion model, the model incorporating the process of capturing and releasing P at GB simulated the increase. Hence, such a process is significant for simulating the temperature dependence.
Kishimoto, Hirotatsu*; Matano, Minoru*; Asakura, Yuki*; Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Kubo, Hirotaka
no journal, ,
 specimens
specimensTakano, Masahide; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Sudo, Ayako
no journal, ,
For the removal operation of fuel debris of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, some material properties of sintered (U,Zr)O solid solution specimens were measured. Their heat capacity and thermal conductivity were determined in the temperature range from room temperature to 1073 K. Micro Vickers hardness and electrical resistivity were also measured at room temperature as a function of U fraction. In addition to these material properties, the correlation between phases and O/M ratios of U-Zr-O system under oxidizing conditions was investigated. In the (U,Zr)
solid solution specimens were measured. Their heat capacity and thermal conductivity were determined in the temperature range from room temperature to 1073 K. Micro Vickers hardness and electrical resistivity were also measured at room temperature as a function of U fraction. In addition to these material properties, the correlation between phases and O/M ratios of U-Zr-O system under oxidizing conditions was investigated. In the (U,Zr)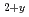 hyperstoichiometric region, the hypothetical O/U ratio in the solid solution was found to be independent of either U fraction and crystal structure. Further, three orthorhombic phases in the U-Zr-O system under more oxidizing conditions were identified, and their phase relationship was successfully defined.
hyperstoichiometric region, the hypothetical O/U ratio in the solid solution was found to be independent of either U fraction and crystal structure. Further, three orthorhombic phases in the U-Zr-O system under more oxidizing conditions were identified, and their phase relationship was successfully defined.
Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Actinide dioxides are the main components of mixed oxide nuclear fuel (MOX). Therefore, in order to develop MOX fuels, we have to have a detailed knowledge of actinide dioxides. However, the determination of their properties through experiments is not easy owing to limitations associated with their handling. In such cases, numerical simulations are effective for the evaluation of the properties of actinide dioxides. So far, we calculated the heat capacity of plutonium dioxide using first-principles density functional theory and successfully reproduced the observed values. In this paper, we apply this calculation method to other actinide dioxides, such as UO , NpO
, NpO and AmO
and AmO , and evaluate their heat capacity. In conclusion, our calculation method is available to evaluate heat capacity of actinide dioxides.
, and evaluate their heat capacity. In conclusion, our calculation method is available to evaluate heat capacity of actinide dioxides.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Noguchi, Yoshihiro*; Kondo, Yoshikazu*; Yano, Kimihiko; Kaji, Naoya; Washiya, Tadahiro
no journal, ,
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko; Nagase, Fumihisa
no journal, ,
Cesium (Cs) chemisorption behavior onto stainless steel (SS) structural materials under LWR severe accident conditions was investigated by means of a chemical equilibrium calculation. Two categories of compounds formed by the Cs-chemisorption onto the SS were identified by a literature review, i.e. Cs-Cr-O and Cs-Si-O system compounds. The chemical stability of Cs-including compounds was evaluated by a chemical equilibrium calculation as a function of oxygen potential. Results showed that Cs-Si-O compounds were stable under a wide range of oxygen potential, while Cs-Cr-O was formed under a limited range. It was also shown that B inclusion might suppress the formation of Cs-Si-O compounds by a formation of Cs-B-O vapor.
Kurata, Masaki
no journal, ,
Outline of METI project on Advanced multi-scale modeling and experimental study for fuel degradation in severe accident is introduced as plenary lecture of NuMat 2014. Individual models, databases and test facilities developed in the project are introduced.
Machida, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Srinivasan, S. G.*; Van Duin, A. C. T.*
no journal, ,
Zircalloy has been widely employed as an excellent material covering the fuel rod. The mechanical and thermal properties have been explored by various experiments. In terms of its use as the fuel cladding, the oxidation reaction is an important topic when exposed to high temperature and high pressure steam in severe accidents. Especially, the hydrogen nucleation accompanied by the oxidation is critical because it leads to the crisis of the hydrogen explosion as observed in the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accidents. Therefore, in this study, we simulate the oxidation reaction in atomistic level by using ReaxFF simulating the chemical reaction in addition to usual molecular dynamics and clarify how the surrounding situation as the temperature and steam pressure accelerates the oxidation reaction and resultant hydrogen nucleation. The advantage using ReaxFF is to directly trace the oxygen diffusion inside Zircalloy depending on the temperature and vapour pressure together with the oxidation reaction. The calculation results reveal that the oxygen diffusion from the top surface to internal area occurs and nucleated hydrogen molecules move out when increasing the temperature above a certain temperature and pressure.
 O
O FCCI barrier on oxide fuel pin of sodium fast reactor
FCCI barrier on oxide fuel pin of sodium fast reactorSasaki, Koei
no journal, ,
(Introduction) Candidate materials of fuel cladding for Gen-IV sodium fast reactor require to develop resistance to fuel cladding chemical interaction (FCCI) for future enhancement of burn-ups ( 20at.%). In this work, we propose a preventive technique of FCCI in oxide fuel pins by Al
20at.%). In this work, we propose a preventive technique of FCCI in oxide fuel pins by Al O
O film coating on fuel cladding inner surface as a FCCI barrier. It has been reported that fission product (FP) corrosions including Cesium, Cesium-Tellurium and Iodine corrosion, play an important role in FCCI behavior based on in-pile and out-pile test results. The Al
film coating on fuel cladding inner surface as a FCCI barrier. It has been reported that fission product (FP) corrosions including Cesium, Cesium-Tellurium and Iodine corrosion, play an important role in FCCI behavior based on in-pile and out-pile test results. The Al O
O film coating on the cladding material surface is able to work as FCCI barrier to protect the corrosive FP elements due to the high chemical stability. (Experiment) In this work, a thin Al
film coating on the cladding material surface is able to work as FCCI barrier to protect the corrosive FP elements due to the high chemical stability. (Experiment) In this work, a thin Al O
O film was experimentally formed on a Fe-12Cr-5Al ternary alloy during heat treatment in controlled atmosphere
film was experimentally formed on a Fe-12Cr-5Al ternary alloy during heat treatment in controlled atmosphere  G
G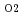 = -870
= -870 -550 kJ/mol at 1173 K for 30 hours. A transmission electron microscope (TEM) image and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping images of the formed Al
-550 kJ/mol at 1173 K for 30 hours. A transmission electron microscope (TEM) image and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping images of the formed Al O
O film are shown in Fig.1. Examinations of Cesium, Cesium-Tellurium and Iodine corrosion were performed on the Al
film are shown in Fig.1. Examinations of Cesium, Cesium-Tellurium and Iodine corrosion were performed on the Al O
O film in order to evaluate its chemical stability. *Cesium/Cesium-Tellurium corrosion test. The Al
film in order to evaluate its chemical stability. *Cesium/Cesium-Tellurium corrosion test. The Al O
O coated specimen was immersed in Cesium or Cesium-Tellurium mixture in analumina crucible and was heated at 923 K for 10 or 100 hours in controlled atmosphere
coated specimen was immersed in Cesium or Cesium-Tellurium mixture in analumina crucible and was heated at 923 K for 10 or 100 hours in controlled atmosphere  G
G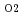 = -420 kJ/mol. *Iodine corrosion test Iodine corrosion test was briefly carried out at 923 K for 10 or 100 hours in an enclosed quartstube containing the specimen and pure iodine chips. (Result) Scanning electron microscope observations and EDX analyses of the specimens after the corrosion tests showed that the corrosions of each corrosive FP element were prevented by the Al
= -420 kJ/mol. *Iodine corrosion test Iodine corrosion test was briefly carried out at 923 K for 10 or 100 hours in an enclosed quartstube containing the specimen and pure iodine chips. (Result) Scanning electron microscope observations and EDX analyses of the specimens after the corrosion tests showed that the corrosions of each corrosive FP element were prevented by the Al O
O coating on the specimens.
coating on the specimens.